Create interactive game with Spring Boot and WebSocket

Why WebSocket
WebSocket is a protocol that enables communication between the server and the browser. It has an advantage over rest HTTP because communications are both bi-directional and real-time. This allows for the server to notify the client at any time instead of the client polling at a regular interval for updates. That’s what we need to design an interactive game. I provided a production-ready project on GitHub and in this post, I want to show you how we can design and develop an interactive game with Spring Boot and WebSocket.
Maven dependency
First, you might need to add the spring-boot-starter-websocket dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-websocket</artifactId>
</dependency>
Enable WebSocket in Spring
I configured WebSocket in WebsocketConfiguration.java :
@Configuration
@EnableWebSocketMessageBroker
public class WebsocketConfiguration implements WebSocketMessageBrokerConfigurer {
@Override
public void registerStompEndpoints(StompEndpointRegistry registry) {
registry.addEndpoint("/sow").withSockJS();
}
@Override
public void configureMessageBroker(MessageBrokerRegistry registry) {
registry.setApplicationDestinationPrefixes("/app").enableSimpleBroker("/topic");
}
}
@EnableWebSocketMessageBroker : It enables WebSocket message handling, backed by a message broker. Here we are using STOMP as a message broker.
The method configureMessageBroker() enables a simple memory-based message broker to carry the messages back to the client on destinations prefixed with “/topic” and also defines the prefix “/app” that is used to filter destinations handled The controller, after processing the message, will send it to the broker.
Similarly,registerStompEndpoints() enables STOMP support and registers stomp endpoints at “/sow”. Doing so, all the WebSocket messages will be channelized through STOMP and this also adds an extra layer of security to the WebSocket endpoint
Remember that, while creating websocket connection from javascipt, we will be using this particular stomp endpoint only.
for enabling SockJs support to provide default fallback option, we need to have this line.
registry.addEndpoint("/sow").withSockJS();
The advantage of using SockJS here is whenever the WebSocket connection is disconnected, or the WebSocket connection can not be established, then the connection will be downgraded to HTTP and the communication between client and server can continue.
Game Endpoints
you can find it in GameController.java
@RestController
@Slf4j
@AllArgsConstructor
@RequestMapping("/game")
public class GameController {
private final GameService gameService;
private final SimpMessagingTemplate simpMessagingTemplate;
@PostMapping("/create")
public ResponseEntity<Game> create(@RequestBody Player player) {
log.info("create game request: {}", player);
return ResponseEntity.ok(gameService.createGame(player));
}
@PostMapping("/connect")
public ResponseEntity<Game> connect(@RequestBody ConnectRequest request) throws GameException {
log.info("connect request: {}", request);
return ResponseEntity.ok(gameService.connectToGame(request.getPlayer(), request.getGameId()));
}
@PostMapping("/connect/random")
public ResponseEntity<Game> connectRandom(@RequestBody Player player) throws GameException{
log.info("connect random {}", player);
return ResponseEntity.ok(gameService.connectToRandomGame(player));
}
@PostMapping("/sow")
public ResponseEntity<Game> sow(@RequestBody Sow sow) throws GameException {
log.info("sow: {}", sow);
Game game = gameService.sow(sow);
simpMessagingTemplate.convertAndSend("/topic/game-progress/" + game.getId(), game);
return ResponseEntity.ok(game);
}
}
For starting a game the first player can use /create rest service to creating a new game. when a game is created, the first player receives a game id and can share this id with the second player. The second player by the game id can call /connect rest service to connect to the specific game. After this, each player can play according to their turn by the /sow service.
The main point here is, when one player plays their turn, the game changes must be sent to the opponent. for this, we send the game object to the game-process topic and in this way, we can sure all subscribers receive the changes as an event.
simpMessagingTemplate.convertAndSend("/topic/game-progress/" + game.getId(), game);
Websocket on client side
To demonstrating my idea I used some simple javascript on client side, so I added these lines on index.html
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/sockjs-client/1.4.0/sockjs.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/stomp.js/2.3.3/stomp.min.js"></script>
SockJS provides the best available fallback options whenever websocket connection fails or unavailable. Following is the sample code to make use of it while establishing websocket connection from a client.
function connectToSocket(gameId) {
console.log("connecting to the game");
let socket = new SockJS(url + "/sow");
stompClient = Stomp.over(socket);
stompClient.connect({}, function (frame) {
console.log("connected to the frame: " + frame);
stompClient.subscribe("/topic/game-progress/" + gameId, function (response) {
let data = JSON.parse(response.body);
console.log(data);
refreshGameBoard(data);
})
})
}
you can find it in socket_js.js
This method always calls when the client creates a new game or connects to a game by id. As you can see if the client receives an event, calls refreshGameBoard() and in this way, we can be sure we have a fresh game board after each player’s turn.
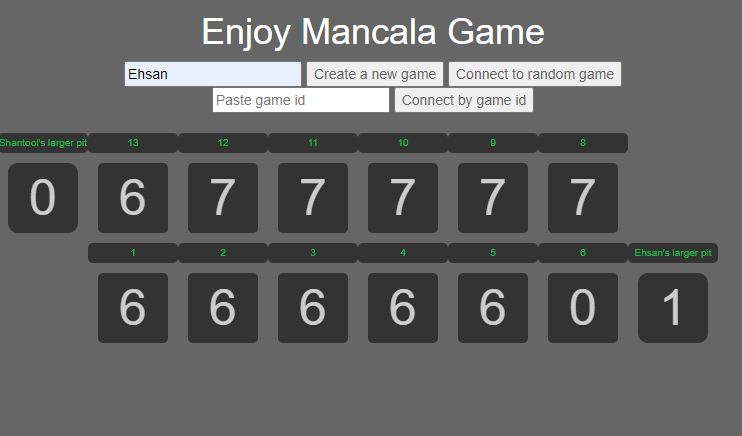
Enjoy Mancala game!
Clone it from GitHub and see other parts like dockerizing and test scenarios.